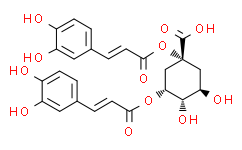
Cynarin inhibits taste receptors, making water to be sweet. It has been shown to have some pharmacological properties including hypocholesterolemic, hepatoprotective, antiviral, antibacterial, and antihistamic effects. Cynarin has marked antioxidant, anticholinergic, reducing ability, radical-scavenging, and metal-binding activities. Cynarin demonstrates 87.72% inhibition of linoleic acid lipid peroxidation at 30 mg/mL concentration. Cynarin exhibits effective DMPD, ABTS, O2, DPPH, and H2O2 scavenging effects, reducing capabilities and Fe chelating effects. IC50 and Ki of cynarin for acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibition are 243.67nM and 39.34±13.88 nM, respectively. Cynarin is a potential immunosuppressant that blocks the interaction between the CD28 of T-cell receptor and CD80 of antigen presenting cells. Cynarin blocks about 87% of the CD28-dependent "signal 2" pathway of T-cell activation under the condition of one to one ratio of T-cell and B-cell. Cynarin binds to the "G-pocket" of CD28 and thus interrupts the site of interaction between CD28 and CD80.
Medlife has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only.


 扫码关注公众号
扫码关注公众号