Title:Salicylate Accumulation Kinetics in Man
标题:人体内水杨酸盐的累积动力学
Authors:Gerhard Levy and Takashi Tsuchiya
作者:Gerhard Levy 和 Takashi Tsuchiya
Journal:New England Journal of Medicine, 1972, Volume 287, Pages 430-432
期刊:新英格兰医学杂志,1972年,287卷,430-432页
Objective:The study investigates the kinetics of salicylate accumulation in humans. Salicylate, the active metabolite of aspirin, is widely used for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Understanding its accumulation in the body is crucial for optimizing dosing regimens and minimizing toxicity.
研究目的:本研究探讨了人体中水杨酸盐的累积动力学。水杨酸盐是阿司匹林的活性代谢物,因其镇痛和抗炎特性广泛使用。理解其在体内的累积对于优化剂量方案和最小化毒性至关重要。
Methodology:
- Participants: Human subjects administered with salicylates.
- Measurements: Blood salicylate levels were measured over time.
- Data Analysis: The kinetics of salicylate accumulation was analyzed to understand its pharmacokinetic properties.
研究方法:
- 参与者:给受试者服用水杨酸盐。
- 测量:随时间测量血液中的水杨酸盐水平。
- 数据分析:分析水杨酸盐的累积动力学以了解其药代动力学特性。
Findings:
1. Absorption and Distribution: Salicylate is rapidly absorbed and distributed in the body.
2. Metabolism: The metabolism of salicylate follows a complex kinetic model, indicating multiple phases of metabolism.
3. Elimination: Salicylate elimination is nonlinear, with higher doses leading to a disproportionately higher plasma concentration.
4. Toxicity Risks: High doses can result in significant accumulation, raising the risk of toxicity.
研究发现:
1. 吸收和分布:水杨酸盐迅速被吸收并在体内分布。
2. 代谢:水杨酸盐的代谢遵循复杂的动力学模型,表明存在多个代谢阶段。
3. 排泄:水杨酸盐的排泄是非线性的,较高的剂量会导致血浆浓度成比例地升高。
4. 毒性风险:高剂量可能导致显著累积,增加毒性风险。
Conclusion:
The study highlights the importance of monitoring blood salicylate levels to avoid toxicity, especially in high-dose or prolonged therapy. The findings suggest that dosage adjustments may be necessary to maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
结论:
本研究强调了监测血液中水杨酸盐水平以避免毒性的重要性,尤其是在高剂量或长期治疗中。研究结果表明可能需要调整剂量以在保持治疗效果的同时最小化不良反应。
Related Compounds and CAS Numbers
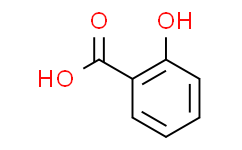
1. Salicylic Acid (Salicylate) - CAS Number: 69-72-7
2. Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) - CAS Number: 50-78-2
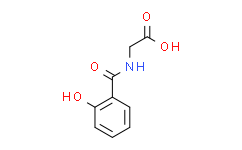
3. Salicyluric Acid - CAS Number: 487-54-7
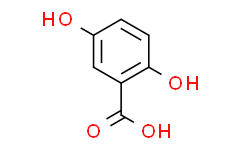
4. Gentisic Acid (2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid) - CAS Number: 490-79-9
5. Phenol (a metabolite of salicylate) - CAS Number: 108-95-2





 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号