Title:Clinical Characteristics, Rapid Identification, Molecular Epidemiology and Antifungal Susceptibilities of Talaromyces marneffei Infections in Shenzhen, China
标题:中国深圳马尔尼菲青霉菌感染的临床特征、快速识别、分子流行病学及抗真菌药物敏感性
Lau SKP, Xing F, Tsang CC, et al.
Journal: Mycoses
Publication Date: May 2019
Volume: 62
Issue: 5
Pages: 450-457
Abstract
This study systematically describes the clinical characteristics, molecular epidemiology, rapid identification methods, and antifungal susceptibilities of Talaromyces marneffei infections at The University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital in Shenzhen, China. Since the hospital opened in 2012, seven cases of Talaromyces marneffei infections have been observed. Three of the patients were local residents of Shenzhen, while four were immigrants from other parts of China. Two patients were HIV-negative but had underlying conditions requiring immunosuppressive treatment. Two out of the seven patients died.
All seven isolates of Talaromyces marneffei were successfully identified using MALDI-TOF MS by extending the internal Bruker database with T. marneffei spectra. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) revealed that the seven isolates belonged to six different new sequence types, demonstrating high genetic diversity. Phylogenetic analysis of concatenated sequences from five loci showed these isolates distributed among other T. marneffei strains. Itraconazole, isavuconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole had low minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for the seven clinical isolates, but anidulafungin had high MICs.
摘要
本研究系统性地描述了在中国深圳市香港大学深圳医院中发生的Talaromyces marneffei感染的临床特征、分子流行病学、快速鉴定方法以及抗真菌药物的敏感性。自2012年医院开业以来,共观察到7例Talaromyces marneffei感染病例。其中三名患者为深圳本地居民,四名为来自中国其他地区的移民。两名患者为HIV阴性,但有需要免疫抑制治疗的基础疾病。七名患者中有两名死亡。
所有七株Talaromyces marneffei通过扩展了内部生成的T. marneffei质谱的Bruker数据库进行MALDI-TOF MS鉴定成功。多位点序列分型(MLST)显示七株菌属于六种不同的新序列类型,显示了高度的遗传多样性。五个基因座的串联序列的系统发育分析表明,这七株菌分布在其他T. marneffei菌株中。伊曲康唑、异葎草醇唑、泊沙康唑和伏立康唑对七株临床分离株的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)较低,但阿尼芬净的MIC较高。
Key Findings
- Clinical Characteristics: Of the seven patients, three were local residents, four were immigrants; two were HIV-negative but had immunosuppressive conditions; two of the seven patients died.
- Rapid Identification: All Talaromyces marneffei isolates were successfully identified using MALDI-TOF MS.
- Molecular Epidemiology: The seven isolates belonged to six different new sequence types, indicating high genetic diversity.
- Antifungal Susceptibilities: Low MICs for itraconazole, isavuconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole; high MICs for anidulafungin.
主要研究结果
- 临床特征: 七例患者中,三例为本地居民,四例为外来移民;两例为HIV阴性,但有免疫抑制性疾病;七例中有两例死亡。
- 快速鉴定: 使用MALDI-TOF MS成功鉴定所有Talaromyces marneffei分离株。
- 分子流行病学: 七株菌属于六种不同的新序列类型,显示了高度的遗传多样性。
- 抗真菌药物敏感性: 对伊曲康唑、异葎草醇唑、泊沙康唑和伏立康唑敏感,但对阿尼芬净耐药。
Significance
- Rapid Diagnosis: MALDI-TOF MS plays a crucial role in the rapid identification of T. marneffei.
- Clinical Management: Highlights the need to consider Talaromyces marneffei infection risk in patients with underlying conditions other than HIV.
- Drug Selection: Provides data on the antifungal susceptibilities of T. marneffei, aiding in clinical decision-making.
研究意义
- 快速诊断: MALDI-TOF MS在快速鉴定T. marneffei方面具有重要作用。
- 临床管理: 提示需要关注除HIV感染外的其他基础疾病患者的Talaromyces marneffei感染风险。
- 药物选择: 提供了不同抗真菌药物对T. marneffei的敏感性数据,有助于临床用药指导。
Compounds and their CAS Numbers
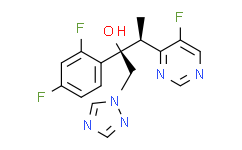
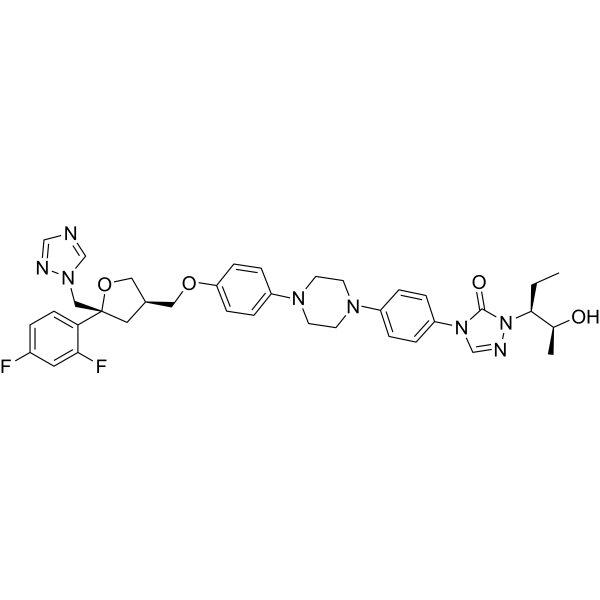
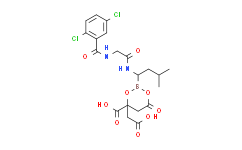
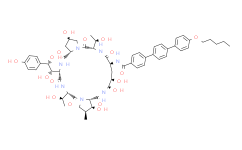
Itraconazole (伊曲康唑): 84625-61-6
Isavuconazole (异葎草醇唑): 241479-67-4
Posaconazole (泊沙康唑): 171228-49-2
Voriconazole (伏立康唑): 137234-62-9
Anidulafungin (阿尼芬净): 166663-25-8






 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号