Title:The role of matrix metalloprotease (MMP) to the autolysis of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus)
标题:基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)在海参(Stichopus japonicus)自溶中的作用
Authors: Zi-Qiang Liu, Yu-Xin Liu, Da-Yong Zhou, Xiao-Yang Liu, Xiu-Ping Dong, Dong-Mei Li, Fereidoon Shahidi
作者: 刘子强, 刘玉新, 周大勇, 刘晓阳, 董秀平, 李冬梅, Fereidoon Shahidi
Journal: Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture
期刊: 《食品与农业科学杂志》
Volume: 99, Issue: 13, Pages: 5752-5759, Publication Date: October 2019
卷号: 99, 期号: 13, 页码: 5752-5759, 出版日期: 2019年10月
DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.9843
Abstract
The study examines the role of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) in the autolysis of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). Autolysis, the self-digestion of tissues by their own enzymes, poses a significant issue for the quality of sea cucumbers. By utilizing various experimental methods, including protein assays and microscopic analyses, the researchers identified and characterized the specific MMPs involved in this process.
摘要
本研究探讨了基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)在海参(Stichopus japonicus)自溶过程中的作用。自溶是组织通过自身酶进行自我消化的过程,对海参的质量影响显著。通过采用多种实验方法,包括蛋白质分析和显微镜分析,研究人员识别并表征了在这一过程中起作用的特定MMP。
Key Points
1. Introduction:
- Importance of understanding autolysis in sea cucumbers for maintaining quality.
- Background on matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) and their known functions in tissue degradation.
- Objective to investigate the specific role of MMPs in the autolysis of Stichopus japonicus.
2. Materials and Methods:
- Materials: Sea cucumber samples.
- Experimental Procedures: Protein extraction, enzyme activity assays, and microscopic analysis.
- Inhibitors Used: EDTA and 1,10-phenanthroline to assess the role of MMPs.
3. Results:
- Protein Levels: Increased soluble protein levels during autolysis indicate active proteolysis.
- Microscopic Analysis: Showed structural changes in sea cucumber tissues over time.
- Enzyme Activity: Confirmed the presence of MMP activity during autolysis.
- Inhibition Studies: Inhibitors reduced the rate of autolysis, supporting the involvement of MMPs.
4. Discussion:
- The study confirms the crucial role of MMPs in the autolysis of sea cucumbers.
- Potential strategies to control MMP activity to improve sea cucumber quality during storage.
5. Conclusions:
- Identification of MMPs as key enzymes in sea cucumber autolysis.
- Implications for the seafood industry in terms of handling and storage practices.
关键点
1. 引言:
- 了解海参自溶对保持质量的重要性。
- 基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)及其在组织降解中的已知功能背景。
- 研究目标是探讨MMP在Stichopus japonicus自溶中的具体作用。
2. 材料与方法:
- 材料: 海参样品。
- 实验程序: 蛋白质提取、酶活性测定和显微镜分析。
- 使用的抑制剂: EDTA和1,10-菲咯啉,用于评估MMP的作用。
3. 结果:
- 蛋白质水平: 自溶期间可溶性蛋白水平增加,表明存在活跃的蛋白水解。
- 显微镜分析: 显示海参组织随时间发生的结构变化。
- 酶活性: 确认自溶过程中存在MMP活性。
- 抑制研究: 抑制剂减少了自溶速率,支持了MMP的参与。
4. 讨论:
- 研究确认了MMP在海参自溶中的关键作用。
- 提出了控制MMP活性以改善海参存储质量的潜在策略。
5. 结论:
- 识别MMP作为海参自溶中的关键酶。
- 对海鲜行业在处理和存储实践中的影响。
CAS Numbers for Key Compounds
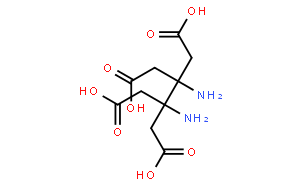
1. EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid): CAS Number: 60-00-4
2.1,10-Phenanthroline: CAS Number: 66-71-7
主要化合物的CAS号
1. EDTA(乙二胺四乙酸): CAS号: 60-00-4
2. 1,10-菲咯啉: CAS号: 66-71-7





 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号