Title:Antinociceptive Activities and the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammation of Asiatic Acid in Mice
标题:亚洲酸在小鼠中的镇痛活性及抗炎机制
Authors: Shih-Shun Huang, Ching-Shu Chung, Hui-Jung Chen, Wei-Cheng Hou, Ming-Jen Sheu, Yuan-Chuen Lin, Pei-Hua Shie, Guo-Jane Huang
作者: 黄士顺、钟敬书、陈慧蓉、侯伟成、许铭仁、林苑全、谢培华、黄国珍
Journal: Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2011
期刊: 证据基础的补充与替代医学, 2011
DOI: 10.1155/2011/895857
Abstract: This study investigates the antinociceptive (pain-reducing) and anti-inflammatory effects of asiatic acid in mice. The results showed that asiatic acid significantly reduced pain in a dose-dependent manner in various pain models. Furthermore, it inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, suggesting that its analgesic effects are due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
摘要: 本研究探讨了积雪草酸在小鼠中的镇痛(减轻疼痛)和抗炎作用。结果显示,积雪草酸在各种疼痛模型中以剂量依赖的方式显著减轻疼痛。此外,它抑制了促炎细胞因子和酶的表达,表明其镇痛效果归因于其抗炎特性。
Introduction: Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene, is known for its pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties. The study aims to explore the mechanisms underlying its antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities.
引言: 积雪草酸是一种五环三萜,因其药理作用(包括抗炎、抗氧化和愈合伤口的特性)而闻名。该研究旨在探讨其镇痛和抗炎活性背后的机制。
Materials and Methods: Mice were used in the study to assess the pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects of asiatic acid. Various pain models, such as the acetic acid-induced writhing test and the hot plate test, were employed. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines were measured using ELISA and RT-PCR techniques.
材料与方法: 研究使用小鼠评估积雪草酸的镇痛和抗炎作用。采用了各种疼痛模型,如醋酸诱导的扭体试验和热板试验。通过ELISA和RT-PCR技术测量炎性细胞因子的表达水平。
Results:
- Asiatic acid reduced the number of writhes in the acetic acid-induced writhing test.
- It increased the latency time in the hot plate test, indicating analgesic effects.
- The compound decreased the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and COX-2 in treated mice.
结果:
- 积雪草酸减少了醋酸诱导的扭体次数。
- 它增加了热板试验中的潜伏期,表明其镇痛效果。
- 该化合物减少了处理小鼠中的TNF-α、IL-1β和COX-2水平。
Discussion: The results suggest that asiatic acid's antinociceptive effects are closely linked to its ability to suppress inflammatory responses. The inhibition of cytokine production and enzyme expression plays a crucial role in its analgesic properties.
讨论: 结果表明,积雪草酸的镇痛效果与其抑制炎症反应的能力密切相关。细胞因子生成和酶表达的抑制在其镇痛特性中起着关键作用。
Conclusion: Asiatic acid exhibits significant antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities in mice, making it a potential candidate for the development of new analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
结论: 积雪草酸在小鼠中表现出显著的镇痛和抗炎活性,使其成为开发新型镇痛和抗炎药物的潜在候选药物。
化合物及其CAS号
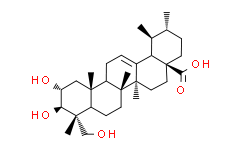
1.积雪草酸(Asiatic Acid)
CAS号: 464-92-6




 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号