Title:Asiatic Acid Induces Apoptosis in SK-MEL-2 Human Melanoma Cells
标题:亚洲酸诱导SK-MEL-2人黑色素瘤细胞凋亡
Authors: Park BC, Bosire KO, Lee ES, Lee YS, Kim JA
作者: Park BC, Bosire KO, Lee ES, Lee YS, Kim JA
Journal: Cancer Letters
期刊: Cancer Letters
Publication Date: January 31, 2005
出版日期: 2005年1月31日
Volume: 218
卷号: 218
Issue: 1
期号: 1
Pages: 81-90
页码: 81-90
Abstract: This study investigates the apoptotic effects of asiatic acid (AA) on SK-MEL-2 human melanoma cells. Asiatic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound found in Centella asiatica, exhibits significant anticancer properties. The research highlights the mechanism through which AA induces apoptosis, focusing on its impact on cell viability, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, protein expression, and caspase activation.
摘要: 本研究探讨了积雪草酸(Asiatic Acid, AA)对SK-MEL-2人类黑色素瘤细胞的凋亡作用。积雪草酸是一种存在于积雪草中的天然三萜化合物,显示出显著的抗癌特性。研究重点介绍了AA诱导凋亡的机制,特别是其对细胞活力、活性氧(ROS)水平、蛋白质表达和caspase激活的影响。
Key Findings:
- Mechanism of Action: AA decreases cell viability and induces apoptosis in SK-MEL-2 melanoma cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): AA significantly increases intracellular ROS levels, which is crucial for its apoptotic effects.
- Protein Expression: AA enhances the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax but does not affect the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. This leads to an altered Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, favoring apoptosis.
- Caspase Activation: The study shows that AA activates caspase-3, a key enzyme in the execution of apoptosis. This activation is inhibited by pretreatment with antioxidants like Trolox, indicating the involvement of oxidative stress in the apoptotic process.
- p53 Independence: Interestingly, AA-induced apoptosis occurs without elevating p53 nuclear protein levels, which are mutated in SK-MEL-2 cells, suggesting a p53-independent pathway.
主要发现:
- 作用机制: AA以时间和剂量依赖的方式降低SK-MEL-2黑色素瘤细胞的细胞活力并诱导凋亡。
- 活性氧(ROS): AA显著增加了细胞内的ROS水平,这是其促凋亡作用的关键。
- 蛋白表达: AA增强了促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达,但不影响抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2,从而改变了Bax/Bcl-2比例,促进了凋亡。
- caspase激活: 研究表明,AA激活了关键凋亡酶caspase-3。该激活过程可以通过抗氧化剂Trolox预处理来抑制,表明氧化应激在凋亡过程中的作用。
- p53独立性: 值得注意的是,AA诱导的凋亡发生在p53核蛋白水平未升高的情况下,而SK-MEL-2细胞中的p53已发生突变,表明其通过p53独立途径发挥作用。
Methods:
- Cell Viability Assay: MTT assay was used to measure cell viability after AA treatment.
- Flow Cytometry: Used to assess the levels of apoptosis by measuring annexin V-FITC/PI staining.
- Western Blotting: Employed to detect the expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase-3 proteins.
- ROS Measurement: DCFH-DA staining was used to measure intracellular ROS levels.
方法:
- 细胞活力检测: 使用MTT法测量AA处理后的细胞活力。
- 流式细胞术: 通过测量Annexin V-FITC/PI染色评估凋亡水平。
- 蛋白质印迹法: 用于检测Bax、Bcl-2和裂解的caspase-3蛋白的表达水平。
- ROS测量: 使用DCFH-DA染色测量细胞内的ROS水平。
相关化合物及其CAS号:
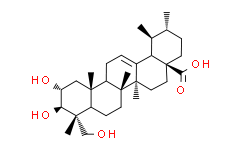
1.Asiatic Acid (积雪草酸)
CAS Number: 464-92-6
2.Trolox (一种抗氧化剂)
CAS Number: 53188-07-1
3.Caspase-3 Inhibitor (Ac-DEVD-CHO) (Caspase-3抑制剂)
CAS Number: 169332-61-0






 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号