Title:Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in man
标题:对乙酰氨基酚(扑热息痛)是人类中的一种选择性环氧化酶-2抑制剂
Authors: Hinz B, Cheremina O, Brune K
作者: Hinz B, Cheremina O, Brune K
Journal: FASEB Journal, 2008
期刊: FASEB Journal, 2008
Volume and Issue: 22(2), pages 383-390
卷号和期号: 第22卷,第2期,页码383-390
Publication Date: February 2008
出版日期: 2008年2月
PubMed ID: 17884974
Abstract:
For over three decades, acetaminophen (paracetamol) was believed to lack significant inhibition of peripheral prostanoids. Attempts to explain its action through inhibition of a central cyclooxygenase (COX)-3 have been dismissed. This study proposes that acetaminophen functions as a selective COX-2 inhibitor. The research involved assessing COX inhibition and pharmacokinetics in five volunteers who received a single 1000 mg dose of acetaminophen orally. Thromboxane B2 (COX-1) and prostaglandin E2 (COX-2) levels were measured in human whole blood both ex vivo and in vitro.
摘要:
在过去的三十多年里,扑热息痛(对乙酰氨基酚)被认为没有显著的抑制外周前列腺素的作用。通过抑制中枢环氧合酶(COX)-3来解释其作用的尝试已经被否定。这项研究提出,扑热息痛作为选择性COX-2抑制剂发挥作用。研究评估了五名志愿者在口服1000毫克扑热息痛后的COX抑制作用和药代动力学。通过体外和体内测量人类全血中的凝血诱导的血栓烷B2(COX-1)和脂多糖诱导的前列腺素E2(COX-2)。
Key findings include:
- Acetaminophen showed a 4.4-fold selectivity for COX-2 inhibition.
- After oral administration, COX-1 inhibition was 56% and COX-2 inhibition was 83%.
- Acetaminophen plasma levels remained above the in vitro IC50 for COX-2 for at least 5 hours post-administration.
- The study concludes that acetaminophen's analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, along with its superior gastrointestinal safety profile compared to NSAIDs, can be attributed to its substantial COX-2 inhibition.
主要发现包括:
- 扑热息痛对COX-2抑制的选择性为4.4倍。
- 口服给药后,COX-1的抑制率为56%,COX-2的抑制率为83%。
- 扑热息痛血浆水平在给药后至少5小时内保持在COX-2的体外IC50以上。
- 研究得出结论,扑热息痛的镇痛和抗炎效果以及相对于NSAIDs的优越胃肠道安全性可归因于其显著的COX-2抑制作用。
Key Compounds and their CAS Numbers
Acetaminophen (Paracetamol): 103-90-2
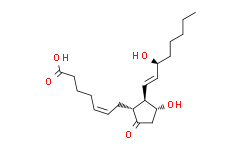
Prostaglandin E2: 363-24-6




 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号