Title:In vivo activity of posaconazole against Mucor spp. in an immunosuppressed-mouse model
标题:在免疫抑制小鼠模型中泊沙康唑对毛霉菌属的体内活性
Authors: Sun QN, Najvar LK, Bocanegra R, Loebenberg D, Graybill JR
作者: Sun QN, Najvar LK, Bocanegra R, Loebenberg D, Graybill JR
Journal: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
期刊: 抗微生物剂与化疗
Publication Date: July 2002
发表日期: 2002年7月
Volume and Issue: Volume 46, Issue 7
卷和期: 第46卷,第7期
Pages: 2310-2312
页数: 2310-2312
Abstract: The study evaluates the efficacy of posaconazole in treating Mucor spp. infections using an immunosuppressed-mouse model. Posaconazole, a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal, showed significant in vivo activity, reducing fungal burden and improving survival rates in the infected mice. The study's findings suggest that posaconazole could be a valuable treatment option for mucormycosis, a serious fungal infection.
摘要: 本研究评估了泊沙康唑在免疫抑制小鼠模型中治疗毛霉菌属感染的疗效。作为一种广谱三唑类抗真菌药,泊沙康唑显示出显著的体内活性,减少了感染小鼠的真菌负荷,提高了其存活率。研究结果表明,泊沙康唑可能是一种有效的治疗毛霉菌病的选择。
Key Findings:
- In vivo Efficacy: Posaconazole demonstrated significant activity against Mucor spp., leading to a reduction in fungal burden in infected mice.
- Survival Rates: Mice treated with posaconazole showed improved survival rates compared to untreated controls.
- Potential Treatment: The results support the potential use of posaconazole for treating mucormycosis, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
主要发现:
- 体内疗效: 泊沙康唑对毛霉菌属表现出显著活性,减少了感染小鼠的真菌负荷。
- 存活率: 接受泊沙康唑治疗的小鼠存活率较未治疗对照组有显著提高。
- 潜在治疗: 研究结果支持泊沙康唑作为治疗毛霉菌病的潜在用途,特别是对于免疫功能低下的患者。
Methodology:
- Mouse Model: Immunosuppressed mice were used to mimic conditions seen in patients susceptible to mucormycosis.
- Treatment Regimens: Various doses of posaconazole were administered to assess its efficacy.
- Assessment: Fungal burden was measured in organ tissues, and survival rates were recorded.
方法学:
- 小鼠模型: 使用免疫抑制小鼠模拟易感染毛霉菌病的患者状况。
- 治疗方案: 给予不同剂量的泊沙康唑以评估其疗效。
- 评估: 测量器官组织中的真菌负荷并记录存活率。
Conclusion: Posaconazole is effective in reducing fungal burden and improving survival in an immunosuppressed-mouse model of mucormycosis. These findings highlight its potential as a treatment option for this severe infection.
结论: 泊沙康唑在减少真菌负荷和提高免疫抑制小鼠模型中毛霉菌病的存活率方面有效。研究结果突显了其作为治疗这种严重感染的潜力。
Compounds and CAS Numbers
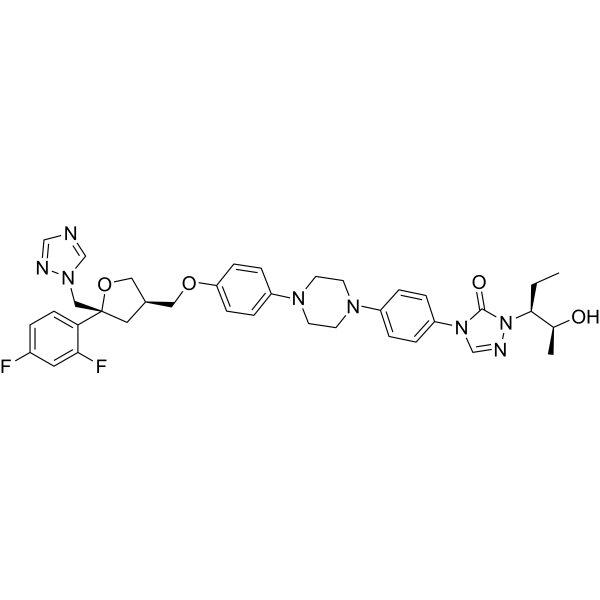
1. Posaconazole (泊沙康唑)
- CAS Number: 171228-49-2
2. Amphotericin B (两性霉素B)
- CAS Number: 1397-89-3




 沪公网安备31011402010657号
沪公网安备31011402010657号